No-Code Automation vs RPA: What’s the Difference?
As businesses look to streamline operations and reduce manual work, automation has become more than a competitive advantage; it’s a necessity. Two technologies are leading this shift: No-Code Automation and Robotic Process Automation (RPA). While both aim to eliminate repetitive tasks and improve efficiency, they differ significantly in approach, use cases, and who they’re built for.
With the rise of user-friendly, no-code platforms and the continued adoption of RPA in enterprise settings, many organizations find themselves asking: Which one should we use and when?
In this blog, we’ll break down the key differences between no-code automation and RPA, explore when to use each, and show how they can work together to create smarter, faster, and more flexible business processes.
What Is No-Code Automation?
No-code automation refers to the use of visual, drag-and-drop platforms that let users build automated workflows without writing any code. These tools are designed for non-technical users, such as operations teams, marketers, HR professionals, and analysts, who want to automate tasks and processes independently of IT or development teams.
Instead of scripting or programming, users create workflows using prebuilt logic blocks, app integrations, and AI modules. These workflows can span multiple cloud-based applications and services, making it easy to automate data movement, notifications, approvals, and more.
What Is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software bots to mimic human actions within digital systems. These bots can interact with applications the same way a person would, clicking buttons, copying data, filling out forms, and navigating interfaces, but much faster and without fatigue.
Unlike no-code automation, which often relies on APIs to connect cloud-based tools, RPA works directly with graphical user interfaces (GUIs). This makes it especially useful for automating legacy systems, desktop apps, and environments that don’t support integration.
Key Differences Between No-Code Automation and RPA
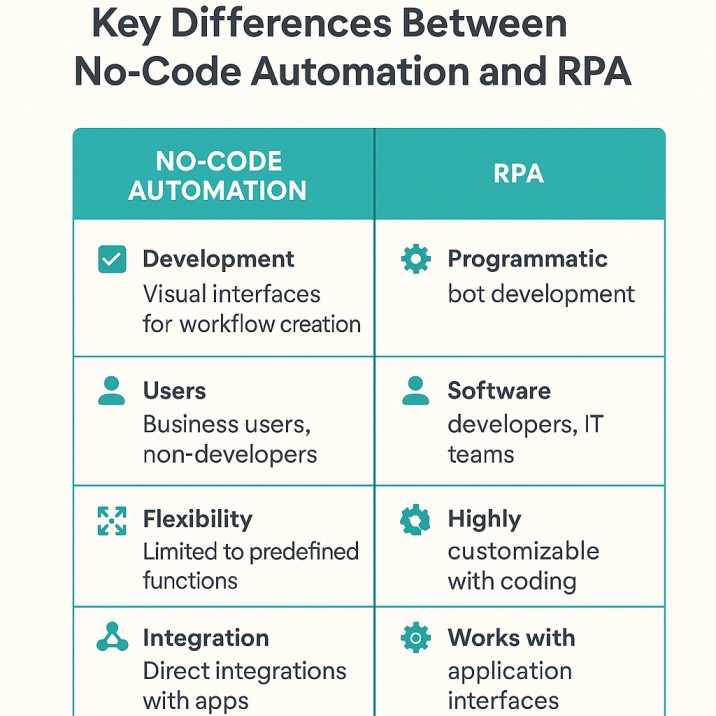
While both No-Code Automation and RPA aim to improve efficiency by eliminating repetitive tasks, they differ fundamentally in their operation, target users, and optimal work environments. Below are the key distinctions that set them apart:
1. Approach to Automation
- No-Code Automation uses visual interfaces and prebuilt integrations to automate tasks across cloud-based apps.
- RPA uses software bots that mimic human actions within applications, often by interacting directly with user interfaces.
2. Ideal Users
- No-Code platforms are built for non-technical users, business analysts, marketers, HR professionals, and citizen developers.
- RPA is typically used by IT teams or RPA specialists, though some tools now offer low-code features for business users.
3. Integration Method
- No-Code Automation relies on APIs to connect tools like Gmail, Slack, Salesforce, and Google Sheets.
- RPA interacts with desktop apps and legacy systems through the graphical interface, not APIs.
4. Use Case Scope
- No-Code Automation excels at cloud-native, cross-app workflows, such as automating lead routing or content publishing.
- RPA is better suited for structured, rule-based tasks like invoice processing, data migration, or ERP automation.
5. Setup and Deployment
- No-Code tools are usually quick to set up, often requiring no technical support.
- RPA deployments can be more complex, involving bot configuration, testing, and orchestration layers.
6. Scalability and Maintenance
- No-Code solutions scale easily across teams with minimal maintenance.
- RPA bots may require frequent updates if UI elements in target systems change.
7. Flexibility
- No-Code offers high flexibility for modern workflows but struggles with apps lacking APIs.
- RPA can automate almost any software, but is less adaptable to dynamic logic or modern cloud stacks.
Summary Table:
| Feature | No-Code Automation | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | Drag-and-drop (visual builder) | Software bot emulation |
| User Type | Non-technical/business users | IT, developers, RPA specialists |
| Integration | API-based | UI-based |
| Best For | Cloud app workflows | Legacy system automation |
| Setup Time | Fast & easy | More complex |
| Scalability | High, with less effort | Requires ongoing maintenance |
Understanding these differences will help you choose the right tool—or combination of tools—for your business needs.
Can No-Code and RPA Work Together?
Yes, No-Code Automation and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can absolutely work together, and when combined, they offer a more complete and flexible automation solution. While no-code tools are ideal for automating tasks across cloud apps using APIs, RPA fills the gaps where integration isn’t possible, especially with legacy systems and desktop applications.
Conclusion
No-Code Automation and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) both aim to streamline operations and reduce manual work, but they do so in fundamentally different ways. No-code platforms empower non-technical users to quickly automate modern, cloud-based workflows using intuitive visual builders. RPA, on the other hand, excels in handling rule-based tasks within legacy systems by mimicking human interactions.
Choosing between the two depends on your specific needs:
- Use No-Code Automation for fast, scalable workflows across SaaS tools.
- Use RPA when dealing with legacy apps, desktop software, or systems without APIs.
- Or better yet, combine both to cover the full spectrum of business automation.
By understanding the strengths of each, organizations can build smarter, more flexible automation strategies that align with both their current infrastructure and future goals.


