AI Agents for Business- What They Are and Why They Matter
AI is rapidly reshaping the way businesses operate, moving from isolated tools and automation scripts to intelligent systems that can understand, decide, and act. At the forefront of this evolution are AI agents- autonomous, goal-driven software programs that perform tasks, make decisions, and interact with users or systems on behalf of a human.
Unlike traditional automation, which follows fixed rules, AI agents combine reasoning, language understanding, and real-time data to execute complex business processes with minimal oversight. From handling customer queries to automating internal approvals, AI agents are helping teams work faster, smarter, and at scale without adding headcount.
In this blog, we’ll explain what AI agents are, how they work, and why they’re important for today’s businesses. We’ll also share real examples, key benefits, and how your company can start using them to work smarter.
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are intelligent, autonomous software programs that can perform tasks, make decisions, and interact with digital systems, much like a human would, but faster and at scale. They are designed to understand objectives, process information, and act independently to complete specific business functions.
Unlike traditional automation tools that rely on rigid rules, AI agents use technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and reasoning engines to respond to changing inputs, learn from feedback, and carry out multi step processes across platforms.
Core Capabilities of AI Agents–
- Understanding goals and context
- Connecting to APIs and enterprise tools
- Making decisions based on rules or data
- Adapting and learning over time
For example, an AI agent in HR might automatically screen resumes, schedule interviews, and update the applicant tracking system, all without human intervention.
In essence, AI agents act as digital co-workers, handling repetitive or intelligent tasks so that teams can focus on higher value work.
Core Components of an AI Agent
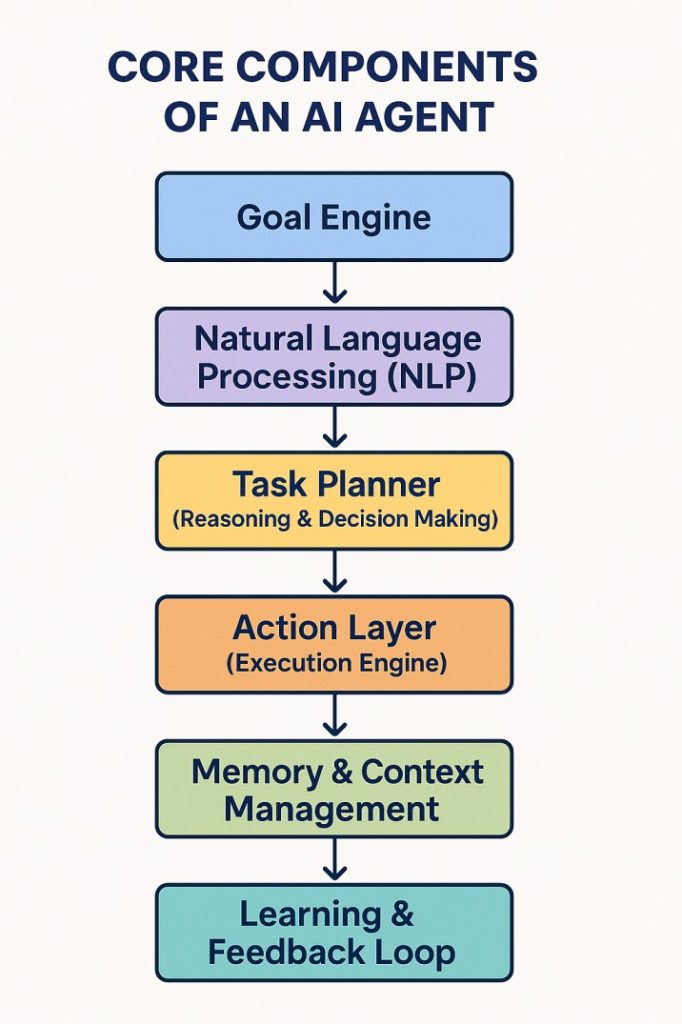
AI agents may appear simple on the surface, answering queries, completing tasks, or interacting with systems, but behind the scenes, they rely on several sophisticated components working together. These core elements give AI agents the ability to reason, act, and adapt in dynamic business environments.
1. Goal Engine (Objective Understanding)
Every AI agent starts with a clear goal or intent, whether it’s processing a support ticket, updating a database, or sending a notification. The goal engine helps the agent interpret user input or system triggers and translate them into specific actions.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
To understand instructions, data, or human queries, AI agents use NLP. This allows them to-
- Interpret written or spoken language
- Extract entities, intent, and context
- Respond conversationally or take relevant actions
3. Task Planner (Reasoning & Decision Making)
Once the goal is clear, the agent needs to figure out how to accomplish it. The task planner determines-
- What steps to take
- In what order
- Based on what rules, priorities, or logic
Some agents use decision trees, others may use machine learning or even generative AI to plan tasks dynamically.
4. Action Layer (Execution Engine)
This is where the agent acts, connecting to APIs, submitting forms, updating CRMs, sending emails, or triggering workflows. The action layer ensures that-
- Tasks are executed correctly and securely
- The agent can interact with multiple systems or databases
- Output is logged and auditable if needed
5. Memory & Context Management
To operate efficiently, AI agents maintain memory of-
- Previous actions or interactions
- User preferences
- Workflow status or past outcomes
This enables them to maintain context over time, personalize actions, and avoid repeating steps unnecessarily.
6. Learning & Feedback Loop (Optional but powerful)
Advanced agents can learn from feedback or outcomes to improve accuracy and efficiency. They can-
- Refine their responses
- Adjust task flows
- Flag edge cases for human review
In essence, an AI agent combines understanding, reasoning, and doing all while maintaining context and improving over time. These components make them ideal for automating high value, repetitive tasks across enterprise environments.
Different Types of AI Agents Explained
AI agents come in various forms, each with a different level of intelligence, autonomy, and complexity. Understanding the types of AI agents can help businesses choose the right approach based on their needs, from basic rule following bots to fully autonomous decision makers.
Below are the most common types of AI agents, typically categorized by how they perceive their environment and act upon it-
1. Simple Reflex Agents
- How they work– These agents respond to specific inputs with pre-programmed rules.
- Example– A chatbot that gives a standard answer when it sees a specific keyword.
- Use case– Basic customer service replies, automated status updates.
2. Model Based Reflex Agents
- How they work– These agents maintain a simple internal model of the world, allowing them to handle more dynamic scenarios.
- Example– An AI agent that updates a dashboard only when new data is detected.
- Use case– Inventory tracking, real time alerts.
3. Goal Based Agents
- How they work– These agents take actions to achieve a defined goal, evaluating outcomes before acting.
- Example– An AI agent that selects the best supplier based on price, delivery speed, and reliability.
- Use case– Procurement automation, intelligent routing.
4. Utility Based Agents
- How they work– These agents not only aim for goals but also prioritize the best possible outcome (maximum utility).
- Example– A customer retention agent that chooses between offering a discount or escalating to a retention specialist based on historical success rates.
- Use case– Personalized marketing, customer experience optimization.
5. Learning Agents
- How they work– These agents learn and improve over time based on feedback, data, or environment changes.
- Example– An agent that refines lead scoring models as it sees which leads convert.
- Use case– Predictive analytics, dynamic process automation, adaptive workflows.
6. Secure & Private AI Agents (Enterprise Focused)
- How they work– Operate within secure, compliant environments, often behind enterprise firewalls, while maintaining full data control.
- Example– An HR agent that handles internal employee data without sending it to third party clouds.
- Use case– Regulated industries like finance, healthcare, and legal.
Each type serves a specific purpose, and often, real world business solutions combine elements of multiple types. As AI agents evolve, businesses can start small and scale toward more intelligent, adaptive systems over time.
How Are Businesses Using AI Agents Today?

AI agents are no longer experimental, they’re actively reshaping how businesses operate across departments and industries. These intelligent agents are being deployed to automate workflows, improve decision making, and deliver faster, more personalized experiences all while reducing manual effort and operational costs.
Here are some of the most impactful real world use cases for AI agents in today’s enterprises-
1. Customer Support Automation
- AI agents handle incoming queries, route tickets, and respond with accurate solutions instantly.
- They reduce response times, improve resolution rates, and free up human agents for complex issues.
- Example– A telecom company uses AI agents to automatically resolve billing and connectivity questions via chat and email.
2. Sales & CRM Management
- AI agents qualify leads, update CRM entries, send follow up emails, and even recommend next best actions.
- They help sales teams focus on high value opportunities while minimizing data entry and follow up delays.
- Example– A SaaS company uses an AI agent to monitor lead activity and send personalized outreach messages automatically.
3. Finance & Accounting Operations
- Agents process invoices, reconcile payments, flag anomalies, and generate reports.
- This reduces human error, accelerates financial cycles, and ensures better compliance.
- Example– An enterprise uses AI agents to match purchase orders with invoices and notify teams of discrepancies in real time.
4. HR and Employee Services
- From resume screening to employee onboarding, AI agents manage tasks that typically consume HR teams’ time.
- They also assist with employee queries and route internal service requests.
- Example– A global company deploys an AI HR agent to schedule interviews, send onboarding documents, and respond to FAQs.
5. IT and Operations
- AI agents monitor infrastructure, respond to tickets, and initiate auto remediation for known issues.
- They integrate with tools like ServiceNow, Jira, and Slack for seamless execution.
- Example– A tech firm uses AI agents to automatically restart servers, assign tickets, and notify engineers based on issue severity.
6. Legal and Compliance Workflows
- Agents scan contracts, extract key clauses, check for policy violations, and maintain audit trails.
- In regulated industries, they ensure that workflows stay compliant and secure.
- Example– A financial institution deploys a private AI agent to review legal documents and flag risky terms.
AI agents are helping businesses do more with less, reducing time spent on repetitive work, increasing accuracy, and enabling teams to focus on strategic initiatives. Whether it’s customer service, operations, or compliance, AI agents are already creating measurable impact across the enterprise.
Key Considerations Before Deploying AI Agents
While AI agents offer powerful advantages from automation and efficiency to 24/7 performance, successful deployment requires thoughtful planning. Before launching AI agents into your business workflows, it’s essential to assess several technical, strategic, and ethical factors to ensure value, scalability, and trust.
Here are the key considerations every organization should evaluate-
1. Data Privacy & Security
- Ensure AI agents comply with data protection laws (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Use secure data storage, encrypted communications, and proper access controls.
- If dealing with sensitive or regulated data, consider private AI agents deployed within secure environments.
2. Scope & Use Case Selection
- Start with tasks that are repetitive, rule based, and high impact.
- Identify business areas where AI agents can deliver measurable outcomes (e.g., cost reduction, faster response times).
- Avoid over automating complex, judgment heavy processes initially.
3. Integration with Existing Systems
- AI agents must integrate smoothly with your CRM, ERP, databases, and communication tools.
- Check API availability and system compatibility early in the planning process.
- Ensure workflows remain connected and traceable.
4. Monitoring, Control & Human Oversight
- Maintain transparency and oversight over AI agent decisions.
- Implement dashboards, audit logs, and manual override options when necessary.
- Combine autonomy with accountability to avoid blind automation.
5. User Experience & Adoption
- Ensure that internal teams understand how AI agents support their work, not replace it.
- Provide training, visibility, and support during rollout to improve adoption.
- Design agents with intuitive interaction flows, especially if employees will be collaborating with them.
The most successful AI agent deployments begin with clarity, control, and collaboration. By addressing these key areas early, your organization can unlock the full potential of AI agents confidently, securely, and at scale.
Conclusion
AI agents are transforming the way businesses operate, turning manual, repetitive tasks into intelligent, automated workflows. By combining autonomy, adaptability, and integration capabilities, these agents empower teams to work faster, make smarter decisions, and scale operations efficiently.
Whether you’re streamlining customer service, managing internal workflows, or enabling smarter data handling, AI agents offer real, measurable value across departments. But like any technology, success depends on thoughtful planning, responsible deployment, and continuous refinement.
As adoption grows, businesses that invest early in secure, well integrated, and goal driven AI agents will be better positioned to lead in an increasingly intelligent and automated world.


